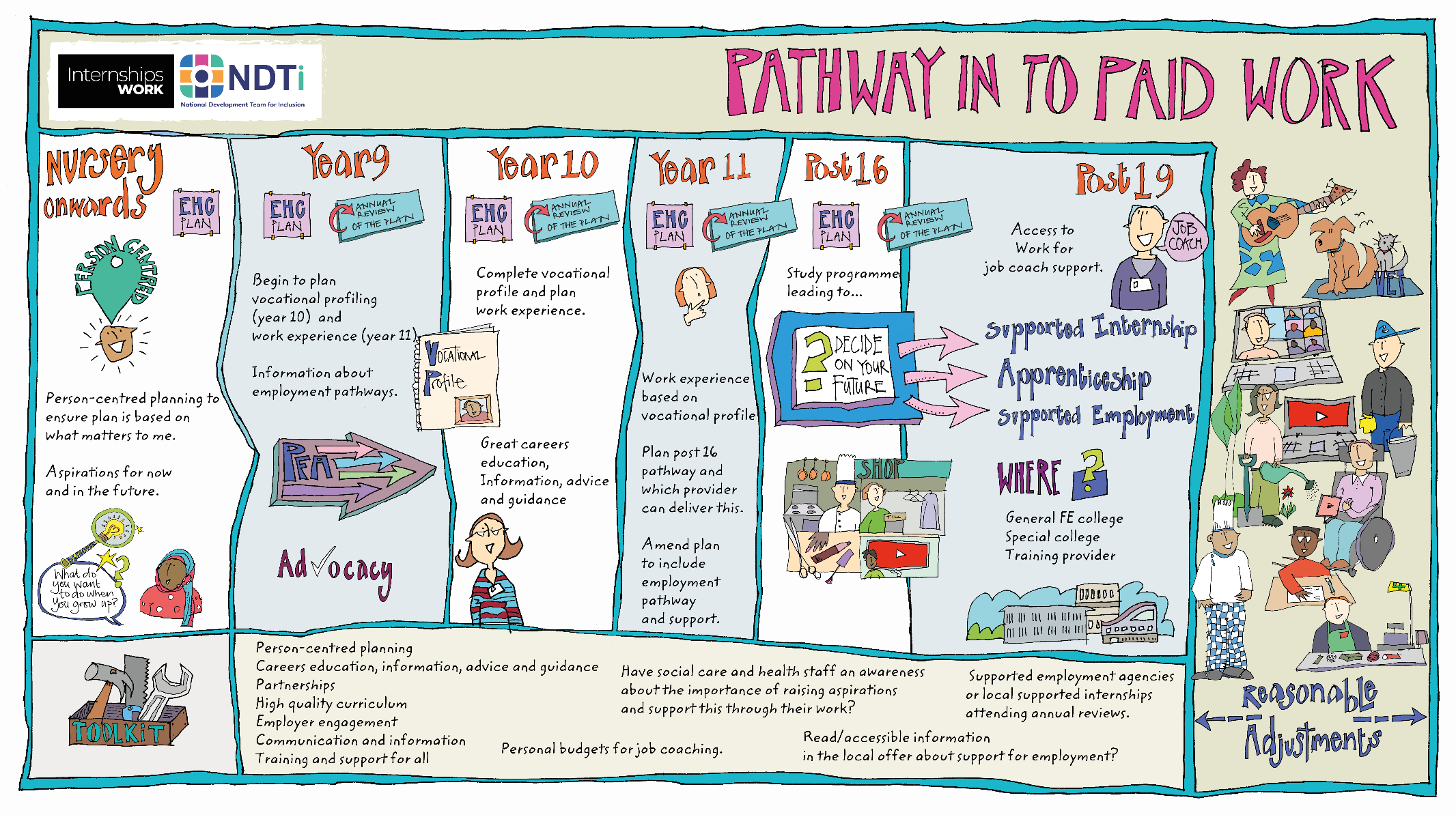
Post 16 Education
Post 16 Education
Please see a list of education option for Post 16 young people with Special Educational Needs and Disabilities:
- Further education
-
Local Colleges have a number of routes that can lead to employment. One option is to undertake academic qualifications (e.g. GCSE’s and A levels) which are accepted entry requirements for some jobs. Alternatively they can lead to into Higher Education and then onto employment.
Another route is to do a vocational (work related) course. These can be in anything from bricklaying and engineering to beauty, tourism and sport. Usually there are different levels of course and entry may depend on GCSE results or other qualifications. These can lead directly to a job or can lead to Higher Education
The final route is through courses run by the special needs departments. Often these courses are at entry level and enable students to have work tasters. They concentrate on gaining the skills they will need for the work place.
Qualifications such as GCSE’s, A Levels, Foundation Degrees and Degrees. Delivered in a variety of settings – schools, colleges and universities. Some jobs and apprenticeships will ask for academic qualifications
- Specialist vocational qualifications
-
Courses that lead to qualifications in particular vocational areas, for example: Hospitality, Engineering, Aviation
These are usually delivered in FE colleges.
Specific work related qualifications – from IT to construction. From level 1 through to level 4. Can work through the vocational levels or enter different levels with academic qualifications. Delivered in a variety settings – colleges, training providers and employers. Not all vocational courses include ‘real’ work experience. If you don’t have GCSE ‘C/4’ or above in Maths and English (under the age of 18), have to continue ‘working towards’. It’s up to providers how courses are delivered so programmes can be from 3 to 5 days per week.
- Higher education
-
Higher Education is a course of study that leads to a degree. Further Education Colleges offer Foundation degrees and Universities offer Honours degrees. Information on courses and entry requirements can be found on the UCAS website. Finance for Higher Education is through the Students loan company. Students with a disability may be entitled to the Disabled Students allowance.
Within the Higher Education sector there continues to be support through disabled students allowance etc.
- Traineeships
-
A traineeship is an education and training programme with work experience. This unlocks the great potential of young people and prepares them for their future careers by helping them to become ‘work ready’.
These are designed to help young people aged 16 to 24 who don’t yet have the appropriate skills or experience. Traineeships provide the essential work preparation training, English, maths and work experience needed to secure an apprenticeship or employment.
A 6 month programme should include 6 months of extended work experience with qualifications. A wide variety of occupational areas and providers locally. Should lead to an apprenticeship or work. Should be ‘working towards’ level 2.
- Study programmes
-
There are a number of local training providers who offer the study programme. Trainees will gain work experience and undertake work related qualifications. If necessary will continue with their maths and English. Trainees may be entitled to a bursary. It is possible within some study programmes for trainees who have additional needs to have 1 to 1 support.
For Newcastle residents with learning difficulties or disabilities there is ‘Working Newcastle’. This is a collaborative programme between Trinity Solutions and the Supported Employment team offering a highly support work focused programme.
Delivered in colleges and training providers across the city. These can be in vocational areas or cover life skills/independent living. Courses usually entry level/level 1. They can and should be highly bespoke to the individual. The whole programme does not necessarily have to be delivered by 1 provider – we have an increasing number of combination offers. Will have to continue working towards maths and English if no ‘C/4’ grade. Should involve some work experience (ideally this should be in a real work environment) if appropriate. What a programme involves and how many days per week will depend on the provider.
- Apprenticeships
-
Apprenticeships give you the opportunity to gain a recognised qualification and develop work related skills. You will earn a salary. There are usually entry requirements as young people need to be working towards at least a level 2 qualification.
Vacancies can be found on the National Apprenticeship website and on the SEND Support, Assessment and Review Team.
At level 2 or above. Placement with an employer. Apprentices receive a wage. Has an education element that is related to the job and this can be delivered either in a College or the work place. A wide variety of occupational areas.
Supported apprenticeships – Newcastle is a pilot area. Maths and English requirements are being reduced for those with EHCPs to entry level 3. Vocational qualification still level 2.
- Supported Internships
-
Supported internships are a structured study programme based primarily at an employer. They enable young people aged 16-24 with a statement of SEN, or an Education, Health and Care plan to achieve sustainable paid employment by equipping them with the skills they need for work, through learning in the workplace.
You can find out more information on Supported Internships by visiting our page here.